Urinary Tract Infection
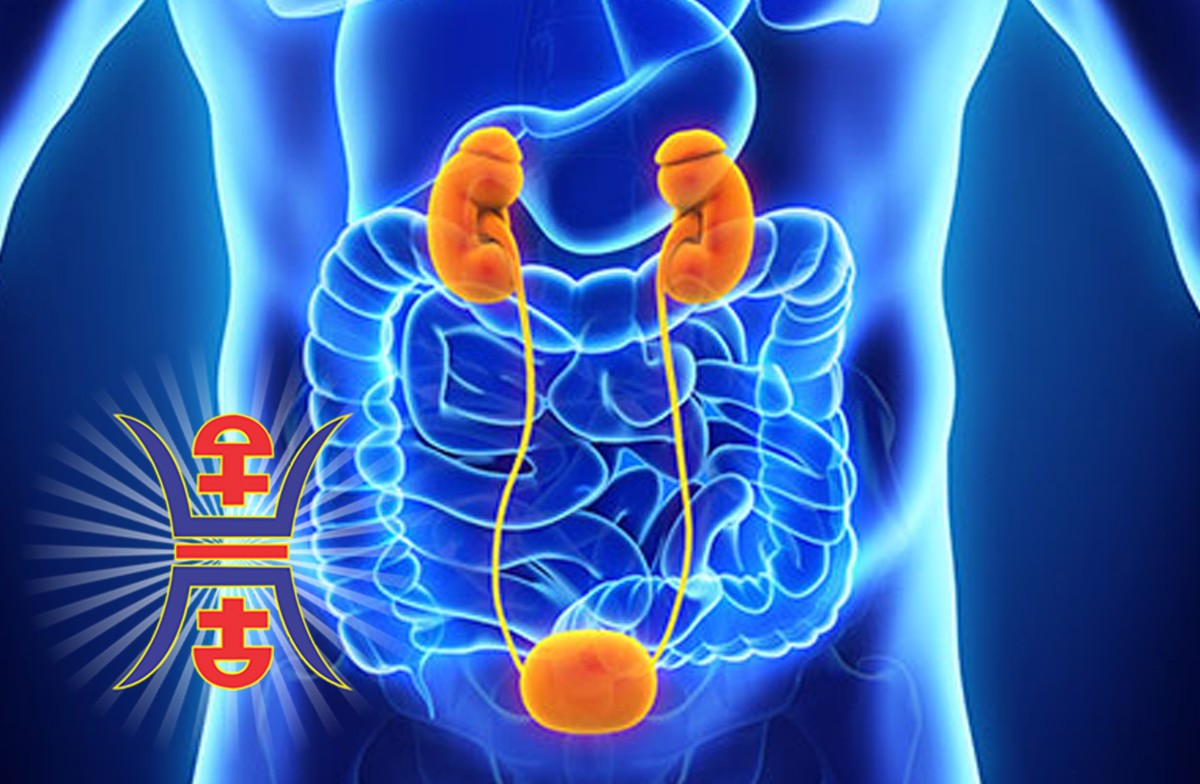
UTI stands for urinary tract infection, which is a common infection that can occur anywhere in the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. UTIs are typically caused by bacteria, but can also be caused by viruses or fungi.
Symptoms of a UTI can include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent or intense urges to urinate
- Cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
- Fatigue or fever (in some cases)
UTIs can be diagnosed through a urine sample that is tested for the presence of bacteria or other signs of infection. Treatment for UTIs typically involves a course of antibiotics, as well as plenty of fluids to help flush out the infection.
To prevent UTIs, it's important to practice good hygiene, such as wiping front to back after using the bathroom and urinating after sexual activity. Drinking plenty of water can also help to prevent UTIs by flushing bacteria out of the urinary system.
In natural health, UTIs are generally believed to be caused by a combination of factors, including external pathogens, such as dampness and heat, and internal imbalances in the body's organs and energy channels.
The kidneys and bladder are considered to be the primary organs involved in the urinary system in natural health, and imbalances in these organs can lead to UTIs. In natural health theory, UTIs are often caused by dampness and heat accumulating in the lower part of the body, which can create an environment where bacteria can thrive and cause infection.
Other factors that may contribute to UTIs in natural health include:
- Emotional stress: Emotions such as anger, frustration, and worry are believed to disrupt the flow of energy in the body, which can weaken the immune system and make it more susceptible to infections.
- Diet: Consuming an excessive amount of spicy or greasy foods, alcohol, and caffeine can create an environment that is conducive to the growth of bacteria and contribute to UTIs.
- Poor hygiene: Failing to maintain good hygiene habits, such as wiping front to back after using the bathroom, can increase the risk of bacterial infections.
- Sexual activity: Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
In Person With Heshoutang Natural Health Members
With Heshoutang Natural Health Online Members
Fill Out the Questionnaire by yourself
According to natural health theory, treatment for UTIs focuses on clearing heat and dampness from the body, promoting urination, and strengthening the overall immune system. Common natural health treatments for UTIs include:
- Herbal remedies: There are many different herbs used in natural health for the treatment of UTIs, including dianthus, gardenia, dianthus, and poria. These herbs can be used in combination to create a formula tailored to the individual's specific symptoms and constitution.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture can be used to stimulate specific points on the body that are believed to help clear heat and dampness and promote urination.
- Dietary therapy: Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help to support the immune system and promote overall health, which can in turn help to prevent UTIs.
It's important to note that while natural health can be a helpful complementary therapy for UTIs, it's not a substitute for medical treatment. If you suspect you have a UTI, it's important to seek prompt medical attention to prevent the infection from worsening.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.













Comments